Best Raid for Fast Database Read Write
RAID is a technology that combines deejay arrays in different forms through predetermined configurations or levels to provide better mistake tolerance, improved performance, and data storage. This configuration, also called RAID levels, is the mode different disks are combined, and this level determines the benefits. Some of the commonly used RAID levels are RAID 0, RAID one, RAID v, RAID 6, and RAID x. There are also other variations depending on the needs of the business.
These RAID levels can be implemented through hardware or software, though most of the higher RAID levels are implemented with hardware for meliorate operation and flexibility.
In this article, we'll compare RAID 10 and RAID v to sympathize which of the two is improve in a given scenario.
What is RAID 10?

Wikimedia
RAID 10 is a complex RAID level that combines the configuration and benefits of RAID 1 and RAID 0. In other words:
RAID ten = RAID 1 + RAID 0
As we all know, RAID i mirrors information and duplicates it for improved mistake tolerance whereas RAID 0 stripes the volume beyond multiple disks for amend performance.
In RAID x, the capabilities of both RAID 1 and RAID 0 are combined to give united states both fault tolerance and enhanced functioning. In this configuration, data is striped evenly across disks, and these are mirrored as well,
Hither is a delineation of this RAID.
Advantages
The advantages of RAID 10 are:
- Offers improved functioning.
- Fast every bit yous can read and write data simultaneously.
- Provides excellent security.
- No data loss.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of RAID 10 are:
- Only 50 pct of storage capacity can be used because data is mirrored.
- Expensive equally it requires more disks to implement.
RAID 5
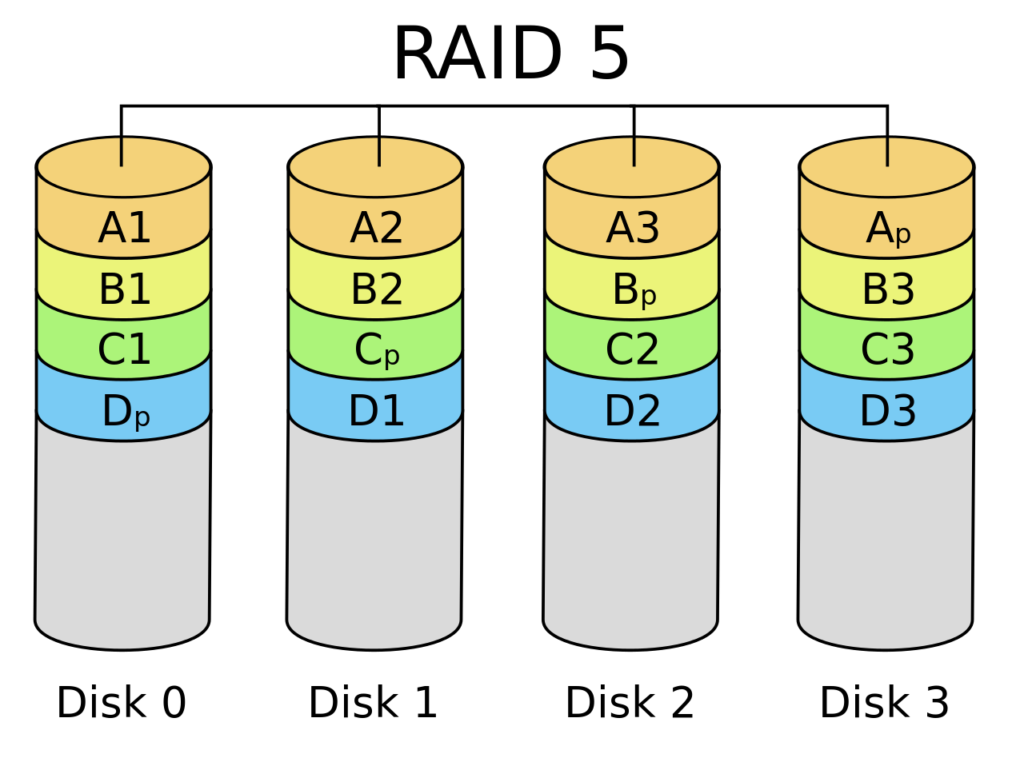
Wikimedia
RAID 5 is a configuration that uses data striping with parity, and this combination easily reconstructs data during a disk failure. Also, since the data is not mirrored, it uses the existing storage more efficiently.
Such a setup also balances functioning, security, storage, and fault tolerance to give an overall efficient configuration. This balance makes it a pop RAID implementation.
Advantages
The advantages of RAID five are:
- Inexpensive to implement compared with other RAID levels.
- Provides fast reads considering of striping.
- Offers a adept residual between security, mistake tolerance, and performance.
- Highly efficient for data storage.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of RAID 5 are:
- Takes a long fourth dimension to rebuild the information because of parity.
- Write performance is dull.
- Circuitous to implement.
So far, we have seen the 2 RAID levels and their advantages and disadvantages. Let's at present motility on to their comparison.
RAID 10 vs. RAID 5: Which is better?
Offset off, there is no question of which RAID level is meliorate every bit each comes with its advantages and disadvantages. Information technology is more about which of the 2 suits your ready or your goal amend for various scenarios.
That said, the biggest difference between RAID ten and RAID 5 is the way information technology rebuilds the data. When a disk fails, RAID x reads data from the mirror disk and copies the same to the disk you lot replaced. Hence, at that place is no alter in your read or write operations.
But in a RAID five configuration, the disk has to read information from all the other disks, use the parity information spread across the disks, and reconstruct the information. This is time-consuming and puts a higher load on your system, thereby increasing the chances of a system crash or even the failure of other disks.
One expanse where RAID 5 scores over RAID 10 is in storage efficiency. Since RAID 5 uses parity information, it stores data more efficiently and, in fact, offers a good balance between storage efficiency, performance, and security. RAID 10, on the other hand, requires more disks and is expensive to implement.
These differences tin can be summarized equally follows:
Operations/Features | RAID 10 | RAID 5 |
| Minimum number of physical disks required | four | 3 |
| Focus area | Performance and fault tolerance | Storage |
| Flexible in structure | Yes | No |
| Read/Write | Faster | Fast |
| Ideal for backup | No | Yes |
| Uses parity | No | Yes |
| Complexity | Depression | High |
| Hardware or software implementation | Works well on whatsoever hardware controller | Can be implemented through software or hardware |
Now that we accept seen the differences, let's see which RAID level to use in different existent-fourth dimension scenarios.
Real-time scenarios
Some common real-time scenarios where we accept to cull a RAID level are described below.
File and application servers
RAID 5 is your best bet for file and awarding servers with a limited number of drivers as it offers a skillful residue between storage, performance, security, and resistance to failure.
Focus on read/write operations
When you lot have applications that crave fast read/write operations, RAID 10 is the right option because information technology doesn't manage parity, so no checks are necessary. In fact, the read functioning of RAID 10 is twice equally fast as RAID five.
Disk failure
If two or more than disks tin can fail in your setup, RAID 5 is your selection, as it's not possible to recover data when two or more disks fail at the same time in RAID 10. While the chances for more than disks to fail at the same time is minimal, it is notwithstanding something to consider.
Simply RAID x reconstructs data faster when a unmarried disk has failed, and so in that location'south no affect to read and write operations whereas RAID 5 takes a long time because of parity checks. Also, data is lost for skilful if the Uncorrectable Read Error (URE) occurs in RAID five.
In all, RAID x is your choice when you want to recover apace from a disk failure without impacting existing operations.
Upkeep and price-effectiveness
If you lot're on a budget or want to get the most out of your money, RAID 5 is your choice considering RAID 10 requires a minimum of 4 disks and uses but fifty percent storage capacity.
Complexity
If you want a elementary RAID setup or if y'all're new to RAID levels and are exploring its benefits, RAID 10 is your pick. You'll accept to simply combine RAID 0 and RAID one to go all the benefits. RAID 5, on the other paw, is complex to implement.
Backup
For efficient fill-in and storage solutions, RAID 5 is the correct choice equally information technology is designed for efficient and cost-constructive storage. It has two-thirds or iv-fifths storage capacity when compared to RAID 10'south 50 pct.
Production and hosting servers
RAID x is ideal for product and hosting servers considering of its functioning and data security. Though it is expensive to implement, it more than makes up for information technology with its functioning and mistake tolerance.
RAID ten works well for database implementations equally well.
RAID 10 vs. RAID 5: At present yous know
To conclude, RAID 10 combines RAID 0 and RAID i to give splendid fault tolerance and performance whereas RAID v is more suited for efficient storage and backup, though it offers a decent level of performance and mistake tolerance. Of course, RAID x is more expensive as it requires more than disks whereas RAID 5 is more than complex to implement.
Since both the RAID levels take varying advantages and disadvantages, the exact choice depends on the given scenario, cost constraints, expectations, and other pertinent factors.
Do you have any experience implementing RAID 10 or RAID v? Please share your experience with our readers in the comments section.
Featured epitome: Shutterstock
More RAID levels articles
- Hackers: the New Ghosts in the Machine
- RAID 5 vs. RAID six: When to use each level and why
- RAID 1 vs. RAID 5: When to use each level and why
- RAID 0 vs. RAID 1: When to utilize each level and why
- Hardware RAID vs. software RAID: Pros and cons for each
Source: https://techgenix.com/raid-10-vs-raid-5/
0 Response to "Best Raid for Fast Database Read Write"
Post a Comment